Hi, this is Jasmine!
First, you must master these two fields: 1. Matter, Chemical Reactions(Matter, Properties, Periodic Table, Atomic Structure, and Compounds) 2. Cells(Cell Reproduction and Protein Synthesis, Heredity and Genetics)
Ok! Let’s start now!
Matter, Chemical Reactions
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. The smallest unit of matter is an Atom(the word comes from Greek and means “cannot be divided”).
Atoms are made of 3 smaller particles(we do not talk about quarks): Protons(+), neutrons(0), and electrons(-). Proton and neutrons stick together to form the center of an atom, the nucleus, which has a (+) charge. Electrons orbit around the nucleus in a certain track but are too fast to pinpoint their exact locations.
The modern atomic model(remember it is a way to represent something we can’t easily see) shows an electron cloud rather than individual electrons like the model we are used to(Bohr’s).
A brief history of the atomic model:
- John Dalton: The first scientist to propose that elements are composed of indestructible atoms. He thought they were so small that we couldn’t see them(absolutely true). He called these particles atoms and his theory on matter was known as the atomic theory of matter(all matter is made up of atoms, and atoms are indivisible[not true] which cannot be created or destroyed, atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical preperties[not true of isotopes], atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties[not true of isotopes], atoms combine in a ratio of a small whole number to form compounds[not true of technology], relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound).
- Sir Joseph John Thomson: J.J.Thomson discovered the presence of (-) charged particles, or cathode rays(electrons) in atoms and pictured them embedded with (+) charged particles, like plum-puddin, so so-called plum-puddin model.[Those people at that time thought cathode rays were light, but only J.J.Thomson thought it was particles]
- Ernest Rutherford: Take a piece of gold leaf, firing “alpha particles” on it. He thought it would be deflected away, but it bounced back. He realized there must be a powerful force between alpha rays and the atoms of gold. The only known force capable of doing this at that time was the electric force. So, he worked out that each atom had a small and heavy (+) charged center, which he called a nucleus. He figured out that electrons are orbiting around the nucleus in mostly space. He called the (+) particles protons.
- Niels Bohr: His theory is: According to Rutherford’s theory, those electrons will orbit around, but if they orbit around there must be force, so eventually they will crash and the atom will disappear; but it doesn’t make sense, so those electrons are in a certain orbit.
- Sir James Chadwick: Rutherford’s student, discovered neutrons in the nucleus.
Each orbit ring of the model are energy level. The closest level to the nucleus can only have 2 electrons and others beyond that can have up to 8.
The way something smells, looks, feels, and tastes are all physical properties. A physical change(size, shape, state) is any change to the physical properties of the matter.
Chemical properties(flammability, reactivity) describe the ability of something to undergo different chemical changes. When any of these chemical properties changes, the matter has gone through a chemical change(signs: color, energy, odor, formation of gas or liquid)
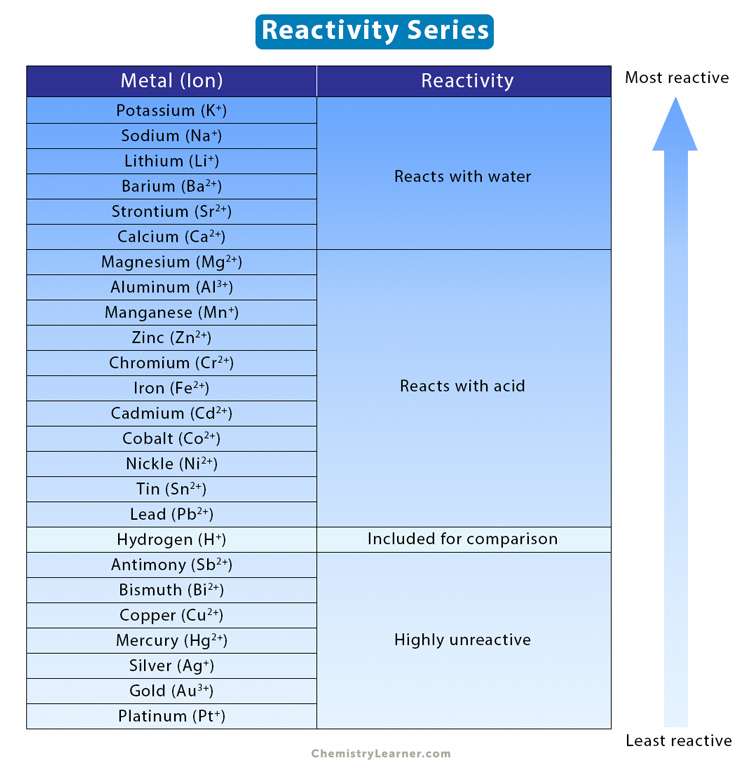
Reactive: whether it will be reacting in a reaction or not
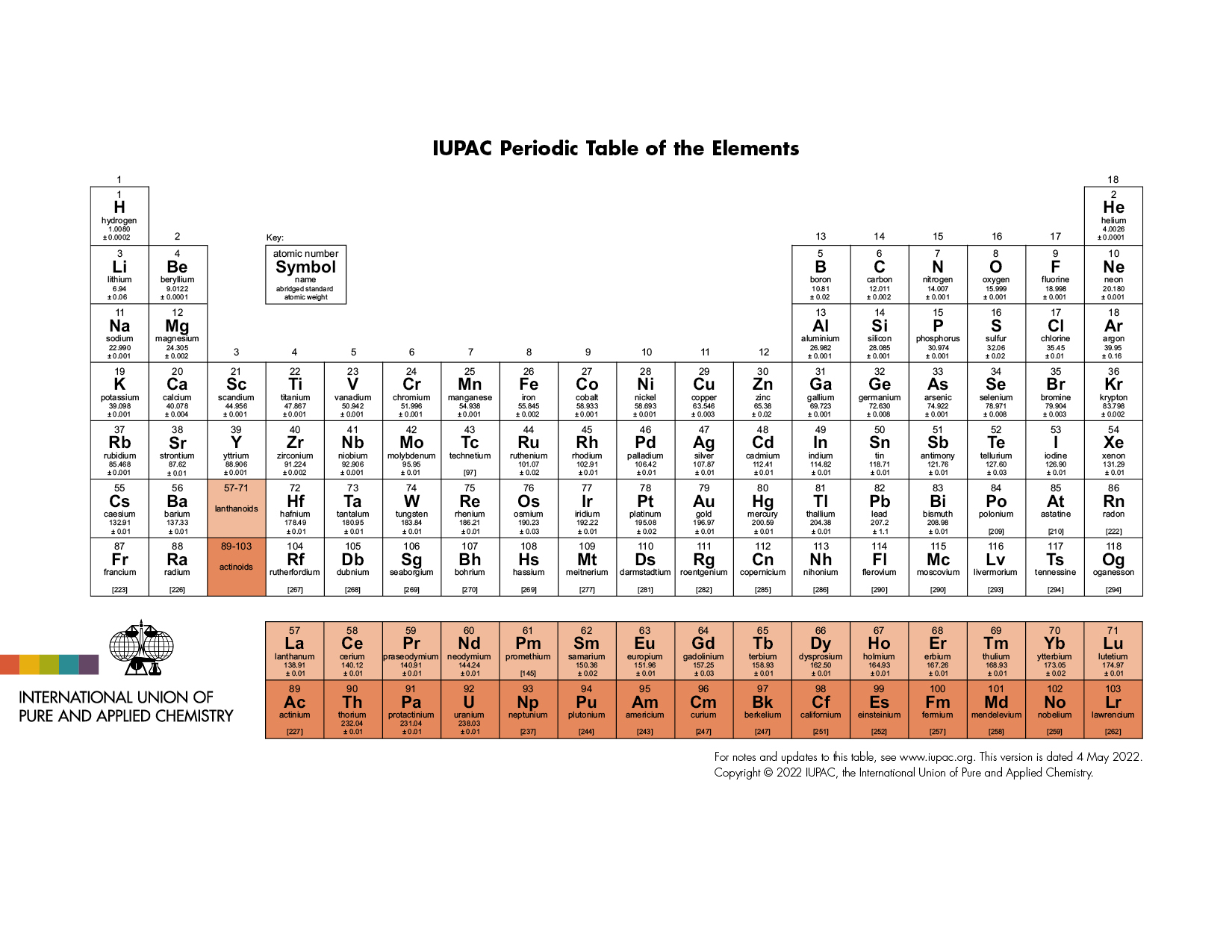
Mendeleev: invented this periodic table. This table can predict elements and elements’ properties, so it is called a genius work. He predicted accurately an element, and it was found after 70 years of his death, Technetium(43). Also, he predicted there would be an element “eka-aluminum” which has an atomic weight of 68, is solid-metal at room temperature, is shiny, conducts very well, has a low melting point, 1cm3 of will 6 grams; and is later found Gallium(31).
Atomic number=proton number(not neutron number!)=number at the top
Period: horizontal row
Group/family: vertical column
atomic mass(every isotopes have different mass)-atomic number=number of neutrons
Conservation of mass: The amount of mass at the start of a reaction=amount of mass after reaction.
Reactant: a substance that is changed in a physical or chemical reaction
Product: the resulting substance of a physical or chemical reaction
Oxidation reaction:
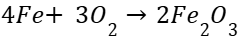
Combustion reaction(all those which look similar):
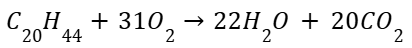
Acid-base reaction: Must have H+and Na
Acid-Metal reaction: Must have H+and metal
Electrolysis: using electric current to drive a chemical reaction and separating the ions in solutions
Ion: atoms that have gained or lost electrons
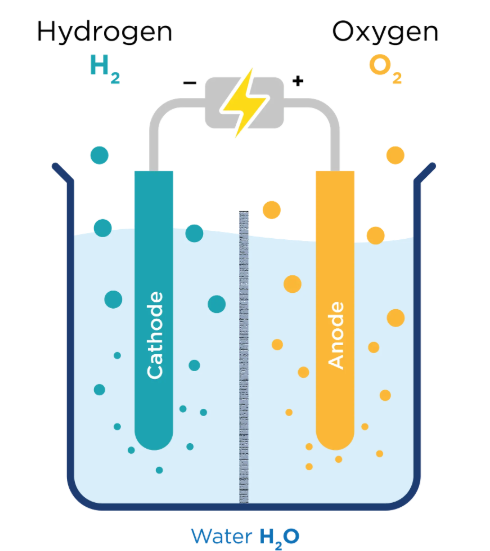
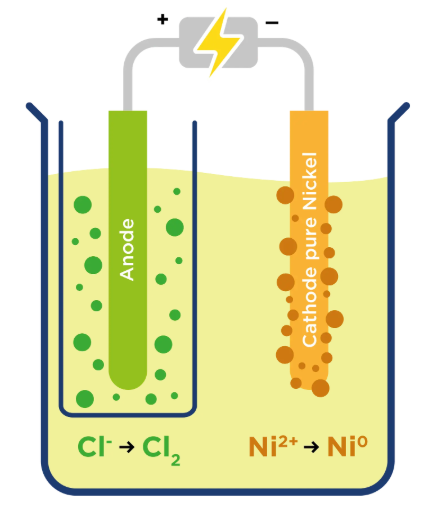
The ones that go to the cathode(-) are cations(+).
The ones that go to the anode(+) are cations(-).
Electrolysis is used in, lithium batteries, water purification, metal plating, and the production of Cl and NaOH.
pH: the potential of hydrogen
Endpoint: the point when it changes color.
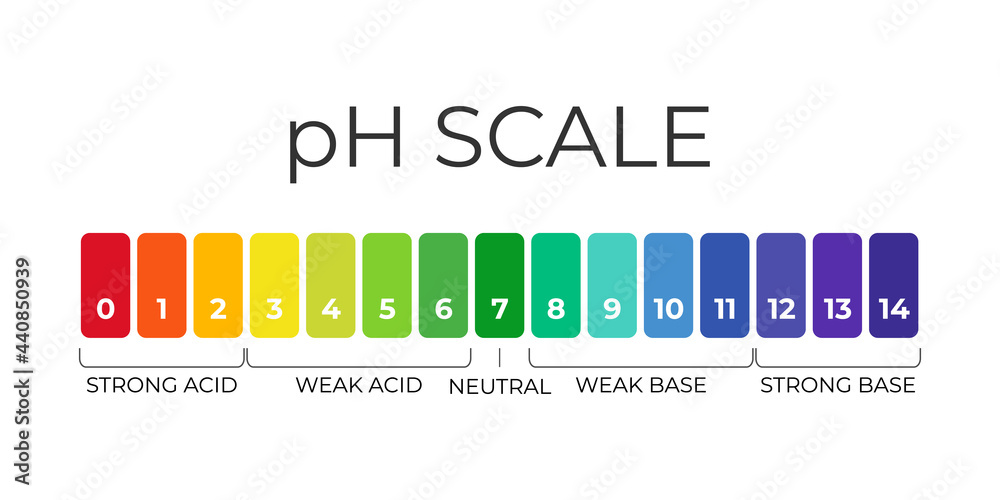
Litmus vs Universal indicator: litmus can only tell us whether it is base or acid, but UI can tell us the level.
Indicator: chemicals used to test other chemicals’ properties
Test CO2 with limewater.
Litmus testing: blue=base, red=acid
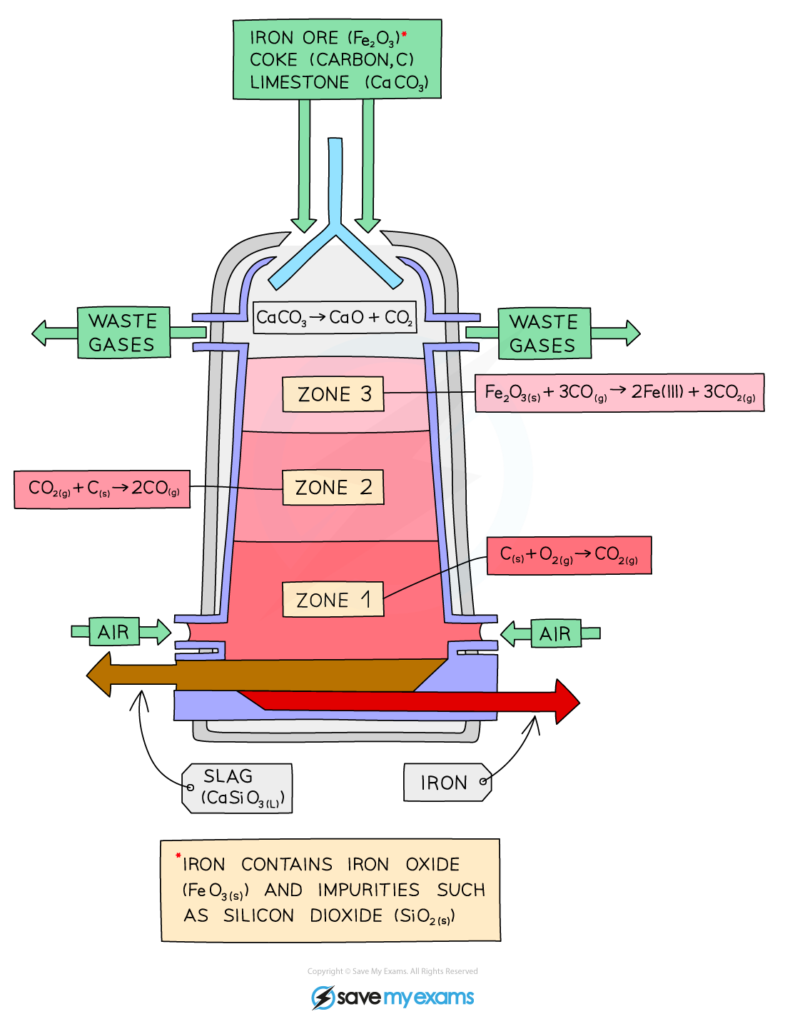
Ore: a combination of rocks, minerals, and metals found in nature
Extracting Fe from iron ore:
- Ore was added along with coke and limestone
- C+O2 turns to CO2
- CO2+C turns to 2CO
- 3CO+Fe2O3 turns to 3CO2+2Fe
- The molten Fe flows to the bottom and is separated from the slag, then can be separated from the furnace.
- CaCO3+C+O turns to slag
As for the history of metals, look at your notes.
Cells
May I not write? It’s too messy.

🙂